All health recommendations related to the cardiovascular system
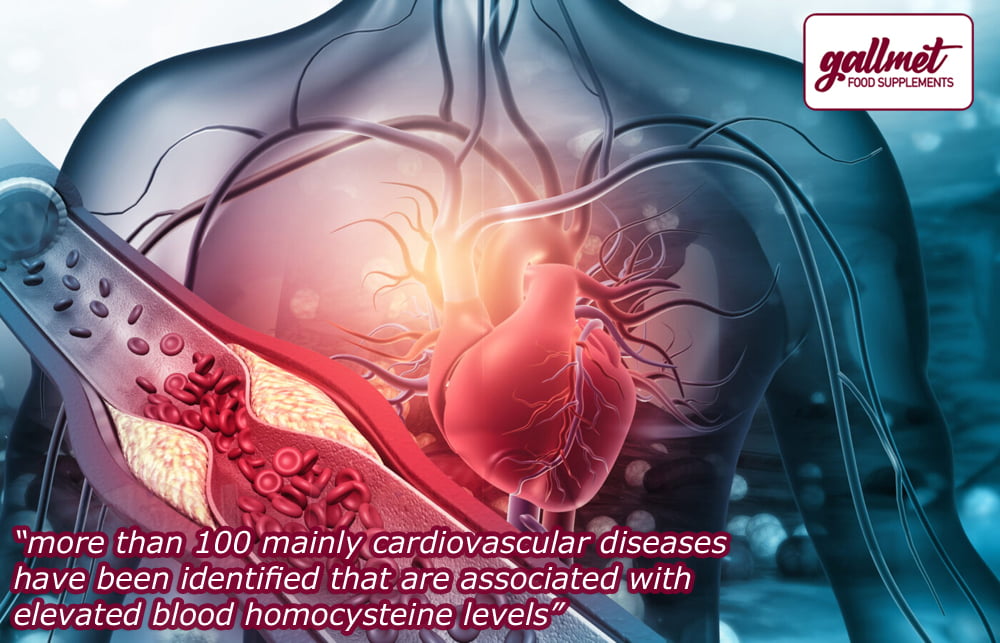
Association of cardiovascular diseases (heart attack, stroke, etc.) with high homocysteine levels
Cardiovascular disease causes almost half of all deaths in Europe! More than 80% of deaths from cardiovascular causes are attributed to heart attacks and strokes, with about 1/3 of deaths occurring in people under 70 years of age. Elevated blood homocysteine levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of traditional risk factors and can be used to predict disease development and assess risk.

Association between diabetes and blood homocysteine levels
While heart attacks have obvious symptoms, many people do not take type 2 diabetes seriously, even though both diseases have the same chance of survival. The latter is not called the “silent killer” for nothing.
Near-normal blood glucose levels can prevent or delay the development of diabetes complications and slow their worsening..

Neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric diseases associated with high homocysteine levels
“Many people think that dementia – a decline in mental performance – is a natural part of ageing that can be almost completely ignored. But this is not entirely true. elevated blood homocysteine levels may be strongly associated with mental decline, and homocysteine levels can be reduced.
In addition, “a few behavioural changes, regular memory activities and creative work can also go a long way in preventing the disease. Nature also offers herbs and vitamins that can help prevent it’...

Association between metabolic syndrome and homocysteine levels
“In metabolic syndrome, the blood homocysteine level is significantly high, which leads to a higher incidence of diseases affecting blood vessels. Homocysteine levels are directly related to age, waist circumference, fasting blood glucose, blood fat and uric acid levels.If you have already developed one of the symptoms of metabolic syndrome, it is likely that other symptoms will also develop over time."...

Association of gout with kidney damage and homocysteine levels in the blood
“Gout (arthritis uricat) can be hereditary, but it can also be caused by diet, alcohol consumption habits, etc., as well as by improper kidney function, enzyme deficiencies, enzyme dysfunction. Blood uric acid levels are not significantly different between gouty and healthy people, but blood homocysteine levels are significantly higher in gout patients."...

About homocysteine - a little biochemistry and history
"Homocysteine is an amino acid that is essential for maintaining normal cellular function, but high homocysteine levels have undesirable effects. There are two ways to get rid of excess homocysteine."...

Tumour diseases and cancer associated with insufficient vitamin B9 (folate) utilisation
"Over the last decades, the number of cases of rectal and colon cancer has increased about 4-fold and has become the second most common malignancy. Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women, with around 350,000 new cases in Europe every year."...

Association between severe coronavirus (Covid-19) infection and high homocysteine levels
"High levels of homocysteine affect the processes that cause severe COVID-19 disease and prevent its treatment. High levels of homocysteine increase the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines in the “cytokine storm”, increase endothelial (inner lining of blood vessels and the heart) dysfunction, inhibit nitric oxide synthesis and lead to thrombus formation. All these pathologies are characteristic of severe SARS-CoV-2."...

Folic acid or folate - what's the difference?
"Although there is a definite difference between the two and their physiological effects are different, the names are often used interchangeably, and even among professionals there is confusion between folate and folic acid."...


